Define and Explain the Different Types of Distribution Transparency.
It enables local and remote objects to be accessed using identical operations. The following are the different transparencies encountered in the distributed systems 3 2.
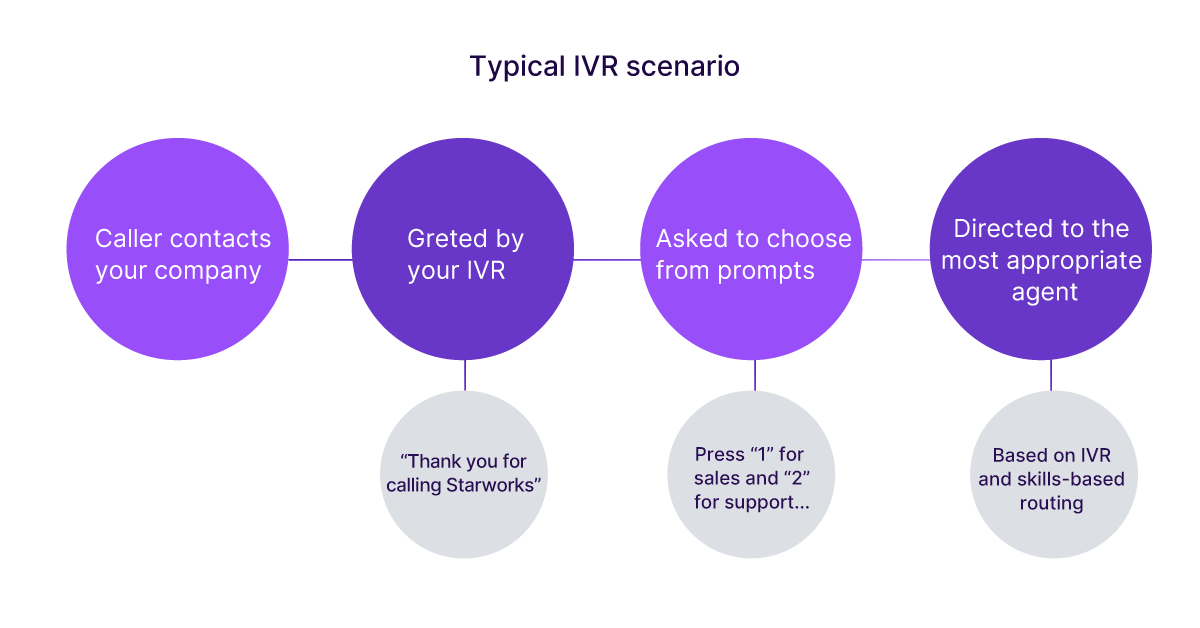
What Is An Acd What To Know About Automatic Call Distribution Talkdesk
Failure transparency - Ensures that the DB will continue to function in.
. This means that the output data from one end of the connection should be the same exact data that arrives as the input to the other side of the connection. 1 - Architectures goal challenges - Where our solutions are applicable Synchronization. Three levels of distribution transparency are recognized.
Distribution transparency provide three levels of transparency. Explain what is meant by distribution transparency and give examples of different types of transparency. Transparency in distributed systems is applied at several aspects such as.
Two Phase Commit Protocol. Because of the distribution transparency the user does not need to know how the data is partitioned and where the data is located. A distributed system contains multiple nodes that are physically separate but linked together using the network.
Transparency in the context of data and communication systems refers to the data stream being sent or the output stream being delivered in the exact bit sequence. Transaction transparency - means transactions will be updated at several sites which in turn will maintain DB integrity 3. If fragmentation transparency is provided by the DDBMS then the user does not need to know.
The standard method to identify the levels of value added or distribution management of course is accountancy provided by any intervening entity in the product service or resource flow. As we know two types of fragmentation are possible horizontally. Location transparency exists when the end user or programmer must specify the database fragment names but does.
Transparency Transparency hides the consequences of distribution Transparency has different dimensions These represents different properties a distributed system might have metric to assess the design of a system Frank Eliassen IfiUiO 16 Access transparency Enables local and remote resourcescomponents to be accessed using identical operations. One fundamental type of distributed system is a clientserver system that splits up functionality into actions by individual components called clients and responses by a provider on the server-side. QExplain what is meant by distribution transparency and give examples of different types of transparency.
Distribution transparency has its 5 types which are discussed below Fragmentation transparency- In this type of transparency the user doesnt have to know about fragmented data and due to which it leads to the reason why database accesses are based on the global schema. Distribution transparencyisthe phenomenon by which distribution aspects in a system are hidden from users and applications. Briefly explain with example how key distribution can be achieved.
Opaque materials either reflect or absorb any incident light. Examples include access transparency location transparency migration transparency relocation trans. Define layer 2 and layer 3 switch in cisco.
Distribution transparency - the DB is seen as one database not a portioned one. What Does Transparency Mean. Various types of distributed systems are used to create those networks that serve people in the ways mentioned above.
DBMS users should not be concerned about the type of DBMS they are using. Wherever is the location. Types of Transparency.
The concept of transparency can be applied to several aspects of a distributed system the most important ones shown in Fig. Any object can be seen through the transparent material. Different forms of transparency in a distributed system ISO 1995.
Define and explain the different types of distribution transparency. One example of transparent material is pure glass. System is called its transparency.
Distributed systems Tanenbaum Ch. Distribution transparency can be classified into. Thus to provide network transparency.
The end user or programmer does not need to know that. Following are three types of transparency. Fragmentation is the highest level of distribution transparency.
Define and explain the different types of distribution transparency. What is difference bw type. It also refers to the.
Transparency to document the various points of resource product or service delivery is typically the domain of the distributor seller or producer. Course Goals and Content Distributed systems and their. Materials which allow complete transmission of light are called transparent.
Access Transparency Local and Remote access to the resources should be done with same efforts and operations. Distribution transparency means a distributed database is consider as a single database. Location transparency User should not be aware of the location of resources.
Posted 7 months ago Discuss the different terminologies used in armature windings. In a distributed database system transparency means that the DDBMS hides all the added complexities of distribution allowing users to think that they are working with a single centralised system. In case of DDBMS the network should not be visible to the user.
Computer Science MCA Operating System. Time coordination decision making Ch. Materials can be classified based on the amount of light they transmit.
In distributed systems transparency is the lack of awareness of users and applications to the presence of the distributed resources. Basic concepts Main issues problems and solutions Structured and functionality Content. Distribution The word distribution has several meanings in the financial world most of them pertaining to the payment of assets from a fund account or individual security to an investor or beneficiary.
Fragmentation transparency Location transparency Replication transparency Local Mapping transparency Naming transparency. Fragmentation transparency is the highest level of transparency. There are different kinds of transparencies that the distributed system has to incorporate.
Each of these nodes contains a small part of the distributed operating system software. All the nodes in this system communicate with each other and handle processes in tandem.

Distributed Databases An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Design Issues Of Distributed System Geeksforgeeks

Distributed Operating System Tutorial Types Examples Advantages Disadvantages

Blockchain An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Query Optimization In Distributed Systems
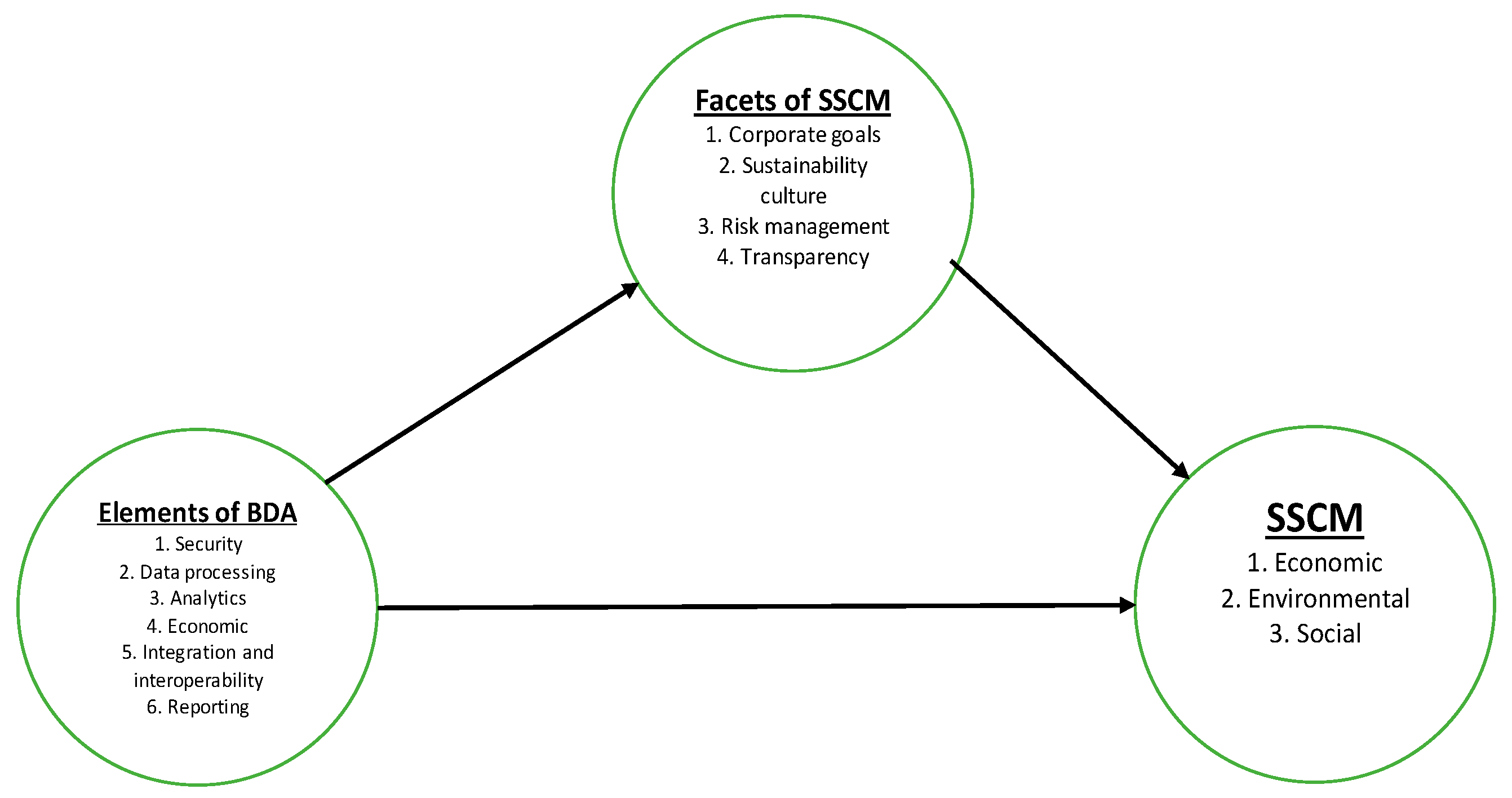
Sustainability Free Full Text Big Data Analytics In Sustainable Supply Chain Management A Focus On Manufacturing Supply Chains Html

Distributed Databases An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
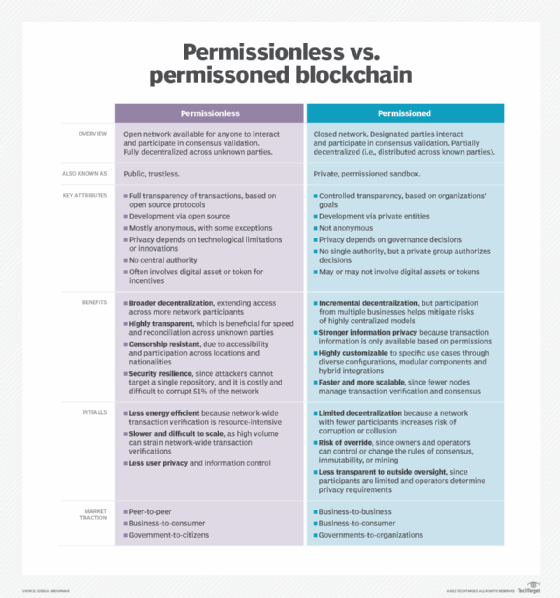
Permissioned Vs Permissionless Blockchains Key Differences

Transparencies In Ddbms Geeksforgeeks

What Are Distributed Systems An Introduction Splunk
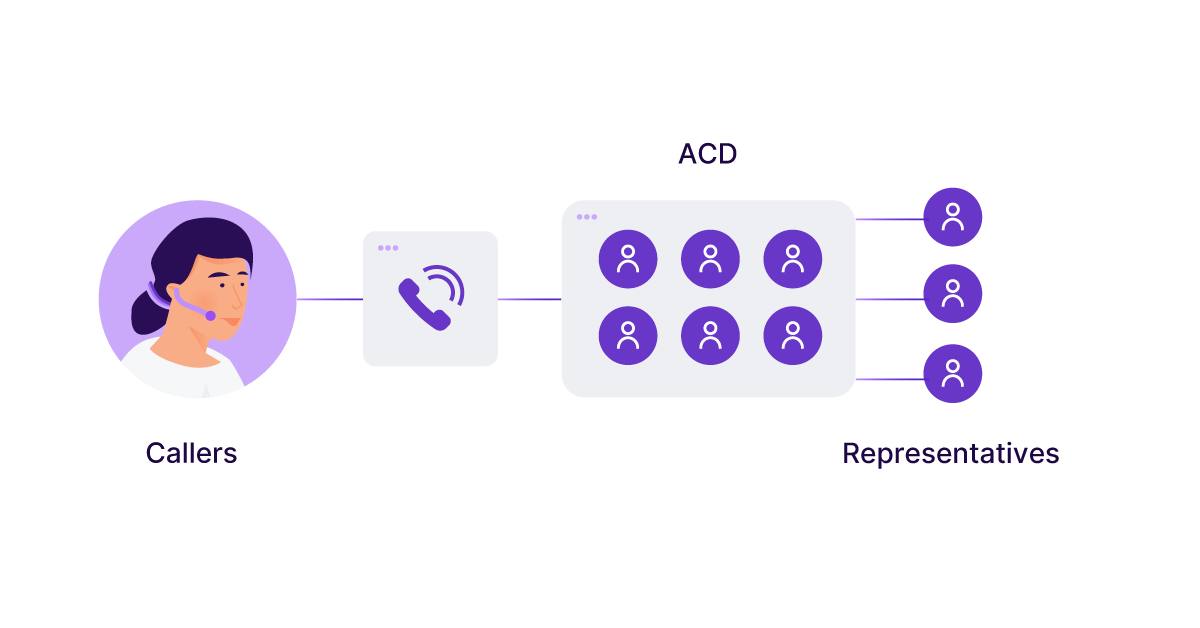
What Is An Acd What To Know About Automatic Call Distribution Talkdesk
Distributed Systems The Complete Guide
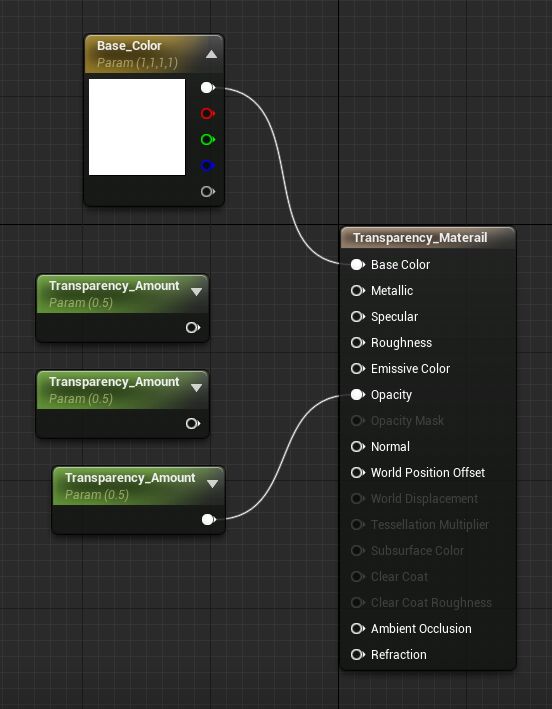
Using Transparency Unreal Engine Documentation

Tech Mahindra Interview Questions Tech Mahindra Recruitment 2022 Interviewbit
![]()
Distributed Systems The Complete Guide
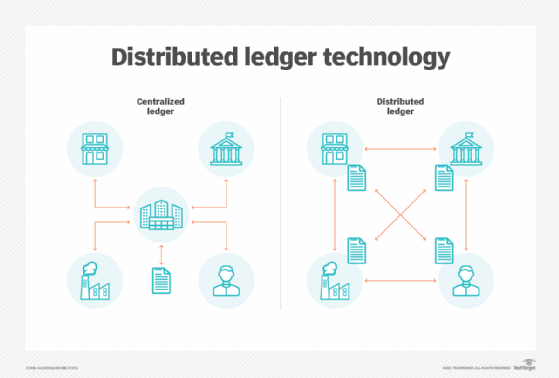
Distributed Ledger Technology Dlt
Distributed Systems The Complete Guide


Comments
Post a Comment