Describe the Cell Nucleus and Its Parts
It is also responsible for the coordination of genes and gene expression. The parts that make up the nucleus include the nuclear envelope nucleolus and chromosomes chromatin.
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
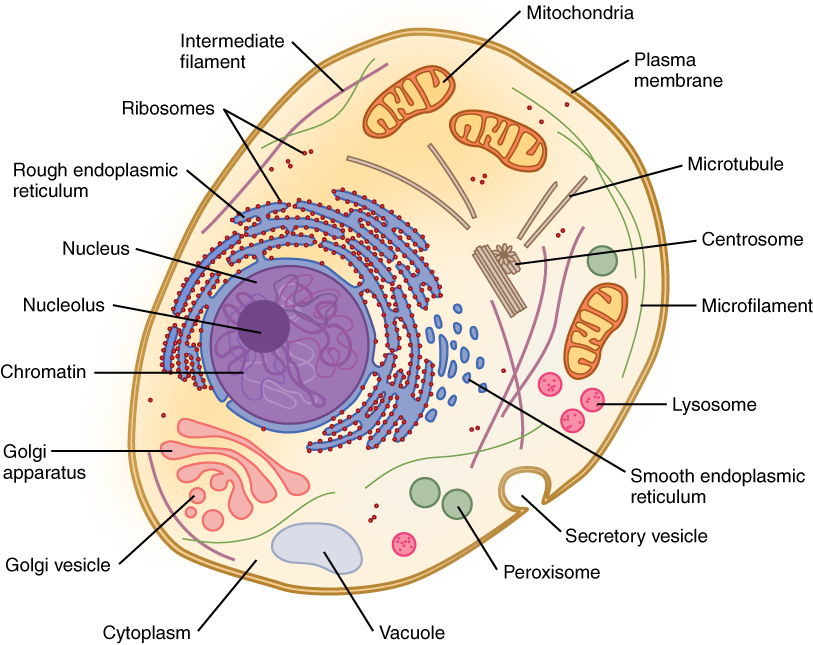
Lysosome acts a digestive system in cells it metabolizes and breaks down wasted organelles or materials in the cell.
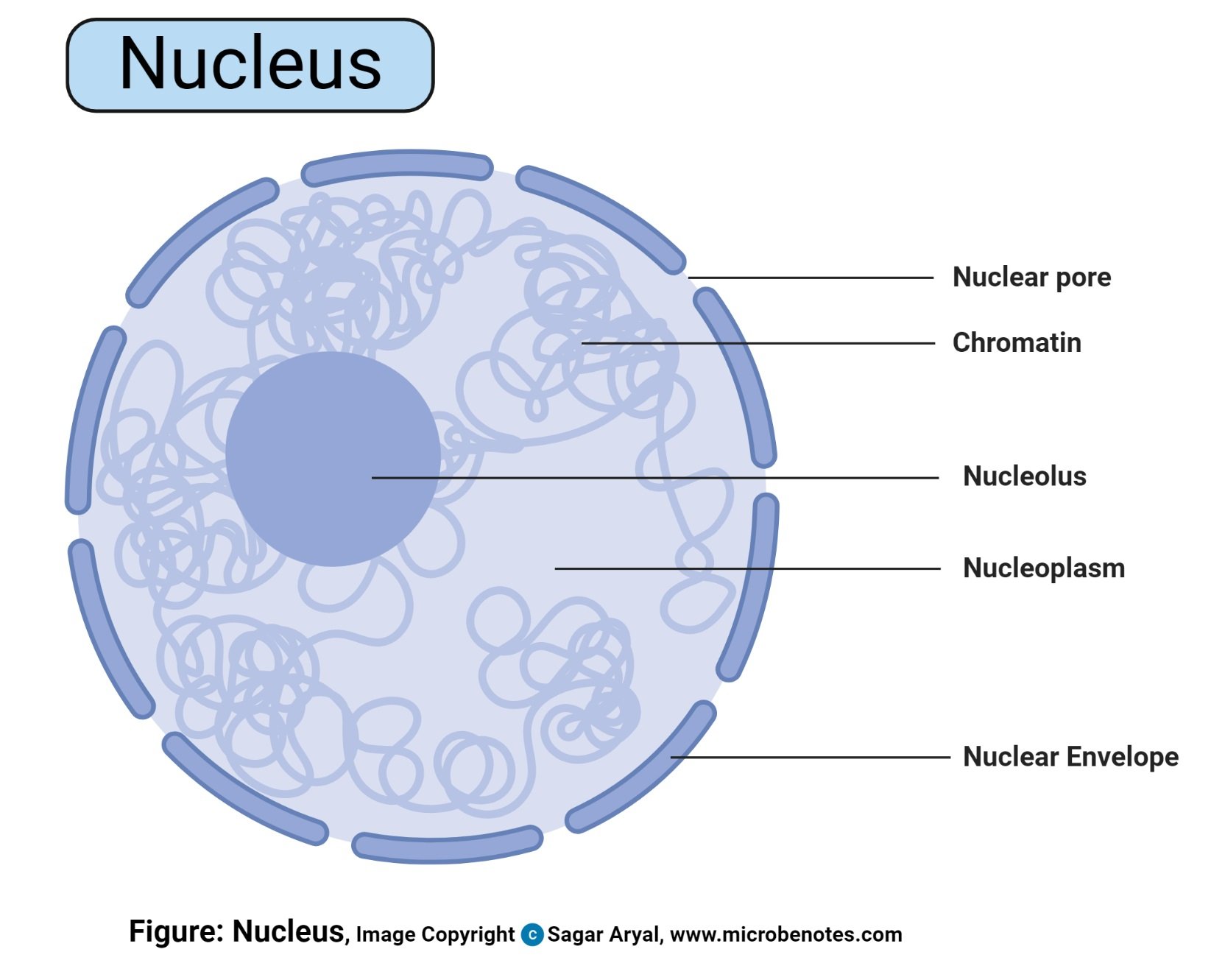
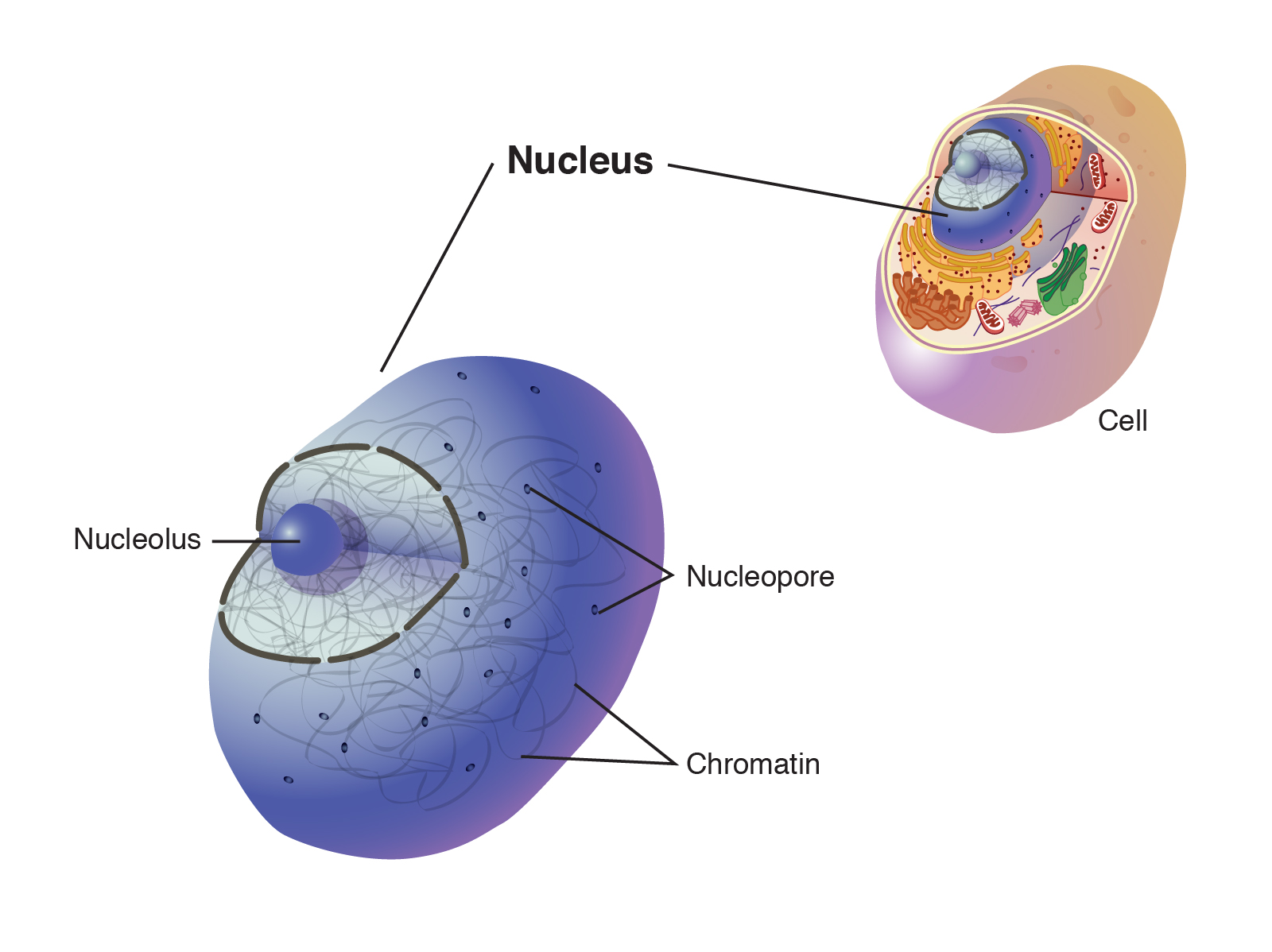
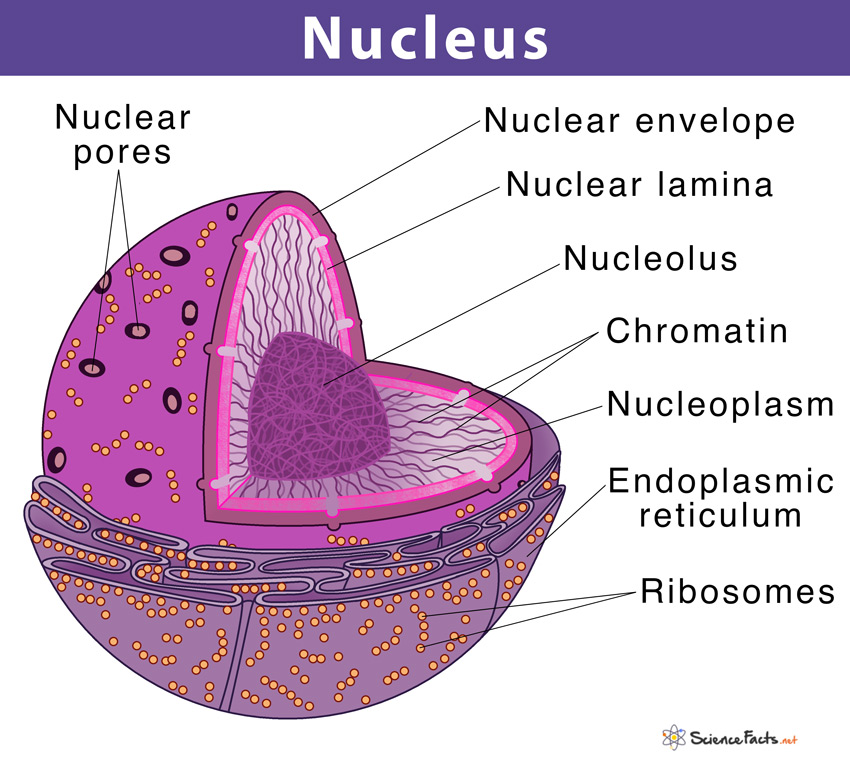
. Structure of the Nucleus STUDY PLAY Describe the nucleus and its components 1. The nuclear envelope also k now n as the nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus and nucleolus. Nuclear Pore 3Nucleolous 4.
Outline the structure of the Nucleus. 2 The main function of the nuclear reticulum is participation in cell-division. Nuclear Pore Round openings in Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus.
Animal Cell Parts And Their Functions The Nucleus. The nuclear membrane- This is an aspect of the nucleus that differentiates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. The nucleus is an example of a cell organelle present in a eukaryotic cell and absent in the prokaryotic cell.
What is nucleus describe its parts and functions. Contains all of the cells DNA except mitochondrial DNA. Nucleus The nucleus contains the hereditary material of the cell the DNA.
The DNA molecules housed in the nucleus also contain blueprints for all of the proteins produced by a cell. The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes. Nucleus is situated in the cytoplasm of the cell.
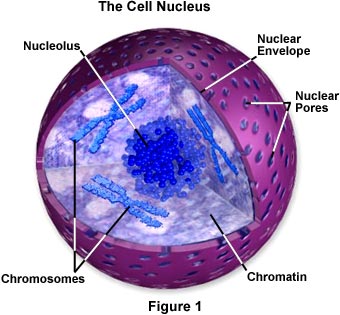
Nucleolus- This is the most important organelle. Atoms are made up of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons in shells. 3 Genes are located in a linear fashion in chromosomes.
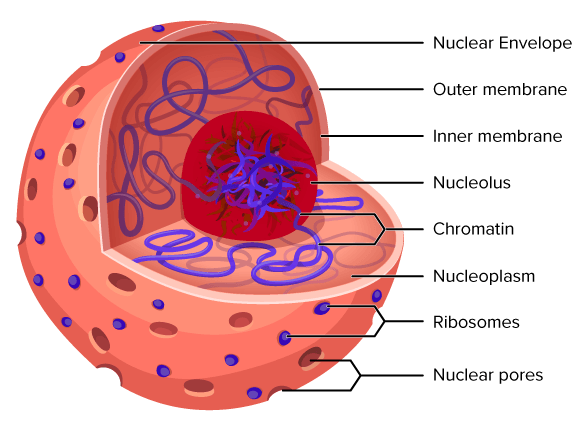
The nucleus is an enclosed organelle that contains the cells DNA. The nuclei of all atoms contain subatomic particles called protons. Nuclear Membrane Nuclear Envelope Encloses nucleus in its inner and outer lipid bilayer.
Up to 24 cash back The Nucleus and Its Parts. The nucleus is a spherical-shaped organelle that is present in every eukaryotic cell. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cells volume.
Microtubule serves as a framework of the cell cytoskeleton. The nucleus protects the DNA and is an integral component of a plants cell structure. The nucleolus helps to synthesize ribosomes by transcribing and assembling ribosomal RNA subunits.
1 The nucleus controls the activities of the cell through its DNA molecule. It is difficult to comprehend just how small an atomic nucleus is but it is much smaller than the width of a human hair and a typical bacterium. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cells volume.
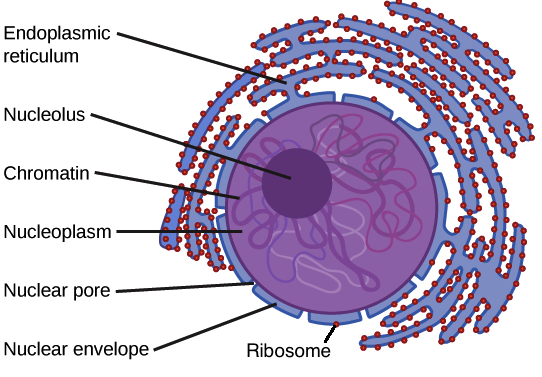
It is surrounded by two porous membranes called nuclear membranes which remain continuous with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Nucleus is a double membrane-bound organelle. This permits the nucleoplasm to interact with the cytoplasm.
Nuclear Membrane Nuclear membrane is double layered and permeable in nature. They contain various entities known as cell organelles that perform various cell functions. Genes control and carry the hereditary characters from one generation to another generation.
Nucleus the control center of each cell. This is an atom Interesting Answer. 15 What is the role of the nucleus in cell division.
The nuclear membrane is perforated by apertures which are. Contains DNA that directs the activities of the cell. The Nucleus is the control centre of eukaryotic cells.
A double-membraned organelle known as the nuclear membraneenvelope engirdles the nucleus. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and houses all of the cells genetic information. Nucleoplasm- It is a type of protoplasm.
It is exclusively found in eukaryotic cells and is also one of the largest organelles. Nucleus lacks the enzymes for aerobic metabolism that are found in mitochondria but it contains enzymes for anaerobic metabolism and for. 12 What is nucleus function.
9 Why is nucleus important in cellular reproduction. Answer 1 of 2. What are the different parts of nucleus class 9.
The nucleus contains a number of enzymes and performs metabolism including synthesis of DNA and various RNAs. 11 Is the nucleus always in the center of a cell. The way atoms are taught in school oversimplify their nature way too much and you can easily understand them better by just thinking of the logic behind it.
Structure of Nucleus Nucleus is covered by a membrane called nuclear membrane and includes numerous components Significant components of nucleus are nucleoplasm chromatin and nucleolus. It sends signals to the cells to grow mature divide and die. The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers the parts of chromosomes carrying the genes for ribosome synthesis.
The genes are composed of DNA. The nucleus of an atoms is literally just the pr. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cells hereditary information and controls the cells growth and reproduction.
The n uclear e. Chromosomes- These are thread-like. The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes.
13 Why is nucleus called controller of the cell class 9. 10 How is the nucleus adapted to its function. Within the nuclear membrane is present a liquid substance called nucleoplasm.
Usually it is round but many different shaped nuclei can be seen in some cells. It is the brain of the cell and controls all of its functions. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope that separates the DNA from the rest of the cell.
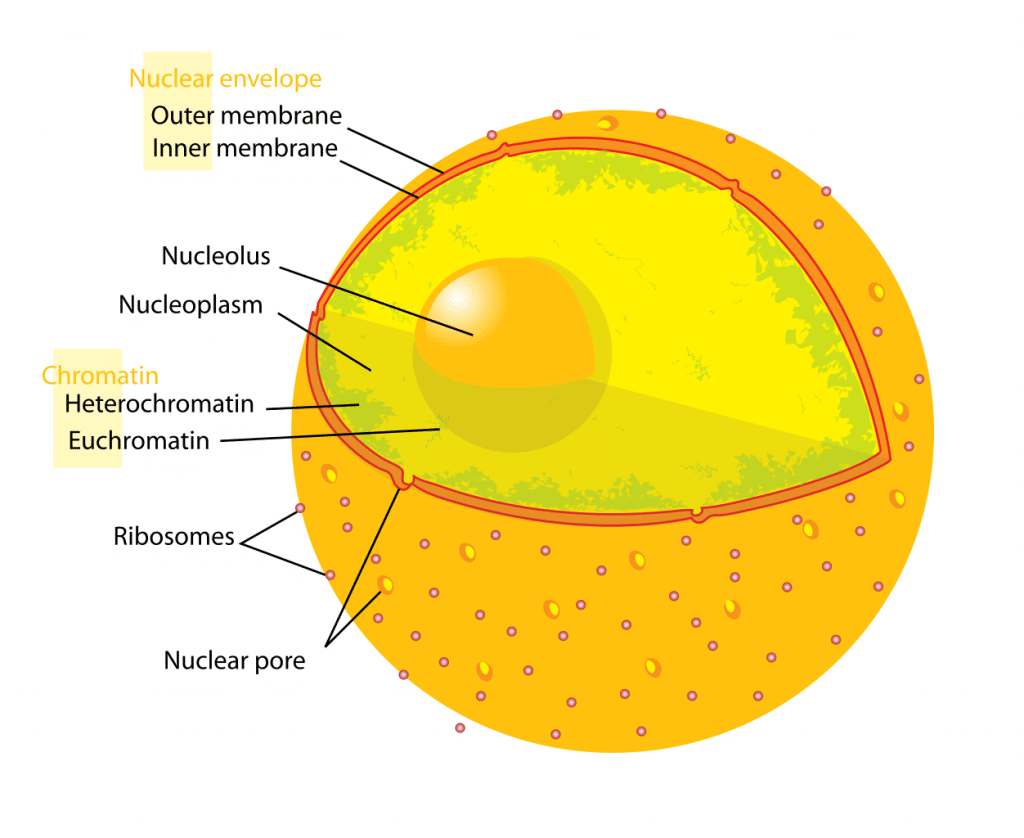
Largest cellular organelle in in eukaryotes 2. Explanation The nucleus is a cell organelle that is characteristic. An outer membrane and an inner membrane that are separated by perinuclear space.
Describe the cell nucleus and its parts - A nucleus is large sphere. 14 Why is the nucleus considered the boss. Contained within the nucleus is a dense membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cells hereditary information and controls the cells growth and reproduction. Introduction A cell represents a basic structural and functional unit of life. It is a membrane bound organelle surrounded by 2 membranes and has a unique well-developed membrane cytoskeleton associated with the inner membrane 3.
Mitochondria acts as the powerhouse of the cell that uses ATP and converts it to energy. The nucleus is composed of many parts that help it function properly within the cell. Describe the cell nucleus and its parts.
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Plant Cell Structure Nucleus

Nucleus Definition Structure Composition Functions Worksheet
Nucleus Structure Function Euchromatin Teachmephysiology
Structure Of A Cell And Its Cellular Components Download Scientific Diagram

Nucleus Definition Function Structure Facts Britannica
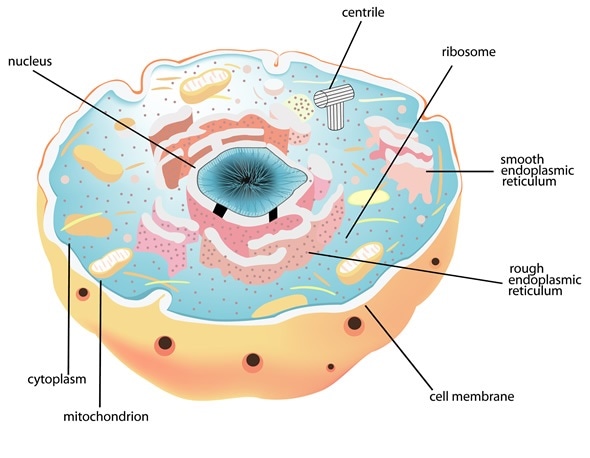
Structure And Function Of The Cell Nucleus
Nucleus Cell Nucleus Nucleus Structure And Functions
Nucleus Its Parts Cell Structure Organelles

Nucleus And Ribosomes Article Khan Academy

Cell Nucleus Function Structure And Under A Microscope Rs Science

5 Main Parts Of Nucleus Biology
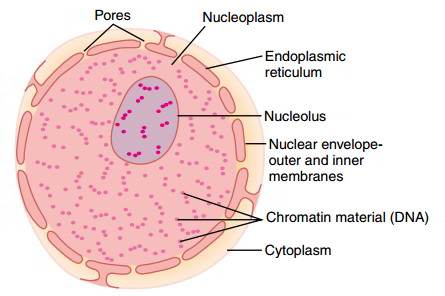
Nucleus Structure Components And Functions Earth S Lab
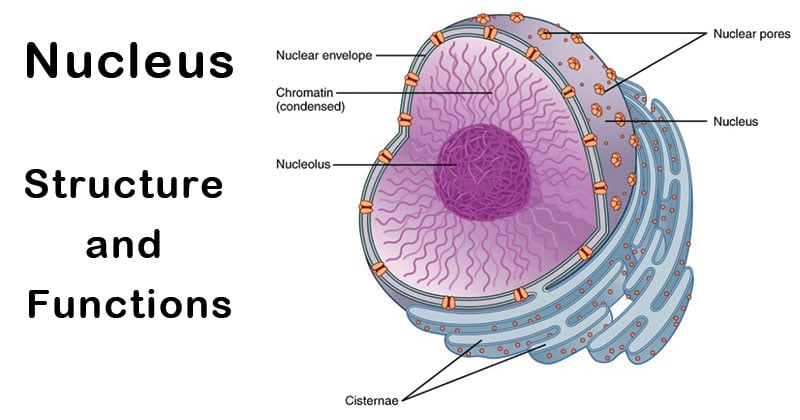
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
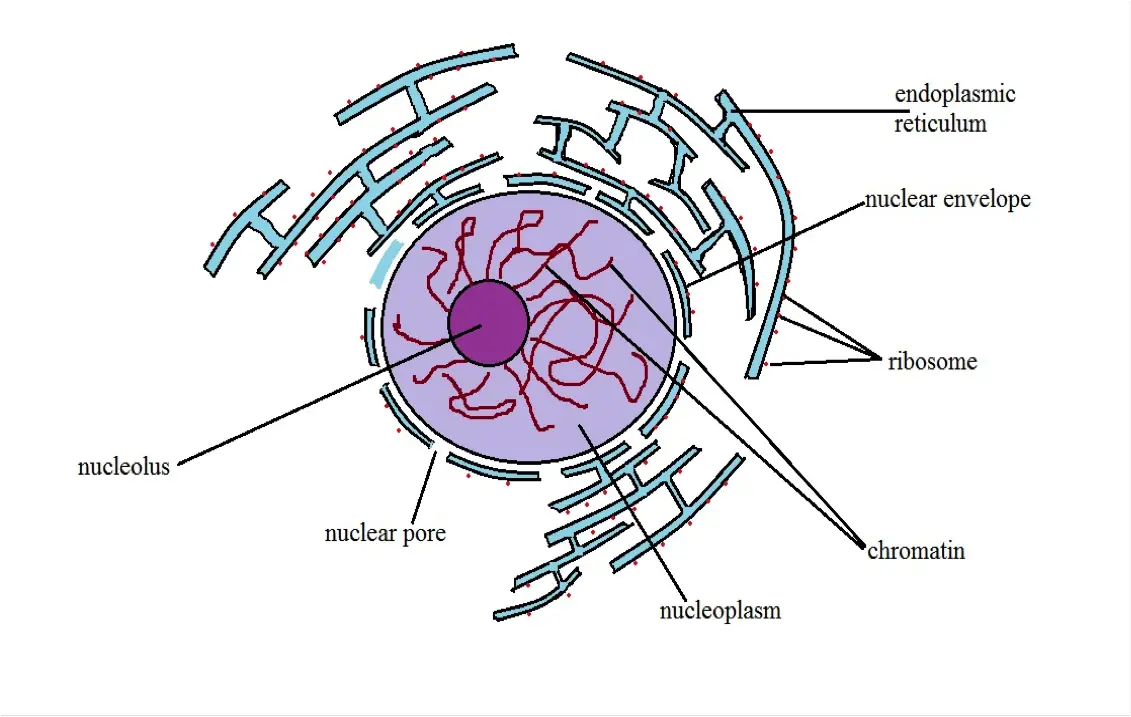
Nucleus Definition Structure Function Cellular Vs Atomic Nuclei

How Nucleus Control Center Of Cell Concept Parts Function Cell Theory Biology Facts Human Cell Structure
Comments
Post a Comment